Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the term Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere. But what exactly does it mean? In simple terms, AI is the ability of computer systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Think of it as making machines “smart” enough to learn, solve problems, make decisions, understand language, and perceive the world around them.
AI isn’t some far-off science fiction anymore. It’s a fundamental part of our daily lives. You interact with AI every time you ask Siri a question, get directions from Google Maps, or receive personalized recommendations from Netflix or even when ChatGPT generates text for you. Understanding the basics of Artificial Intelligence is becoming increasingly important for everyone navigating the modern world.
A Short History of AI
The journey of Artificial Intelligence began in the 1950s, a period of great optimism about the potential of computing. Early pioneers envisioned machines capable of true thought. While the initial progress was slower than anticipated, this era laid the groundwork for future advancements.
Major milestones in AI development include the creation of early problem-solving programs, the rise and fall of “expert systems” in the 1980s, and the resurgence of AI in the late 20th and early 21st centuries with advancements in data and computing power. The evolution has been remarkable, moving from basic automation to sophisticated machine learning algorithms that can learn from vast amounts of data.
How Does AI Work? (Simplified)
At its core, AI operates through a few key principles:
- Data Collection and Patterns: AI systems learn by analyzing large amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. The more data an AI system processes, the better it can become at its task.
- Algorithms and Learning Models: Algorithms are sets of rules or instructions that enable AI to learn from data. Different types of algorithms, known as learning models, are used for various tasks, such as predicting outcomes, classifying information, or generating text.
- Training vs. Inference: AI models are first “trained” using historical data. During training, the algorithm adjusts its internal parameters to improve its performance on the given task. Once trained, the model can be used to make predictions or decisions on new, unseen data – this is called “inference.”
- The Role of Big Data and Computing Power: The recent explosion in AI capabilities is largely due to the availability of massive datasets (“big data”) and the powerful computing resources needed to process this data and train complex AI models.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
To better understand AI, it’s helpful to categorize it into different types:
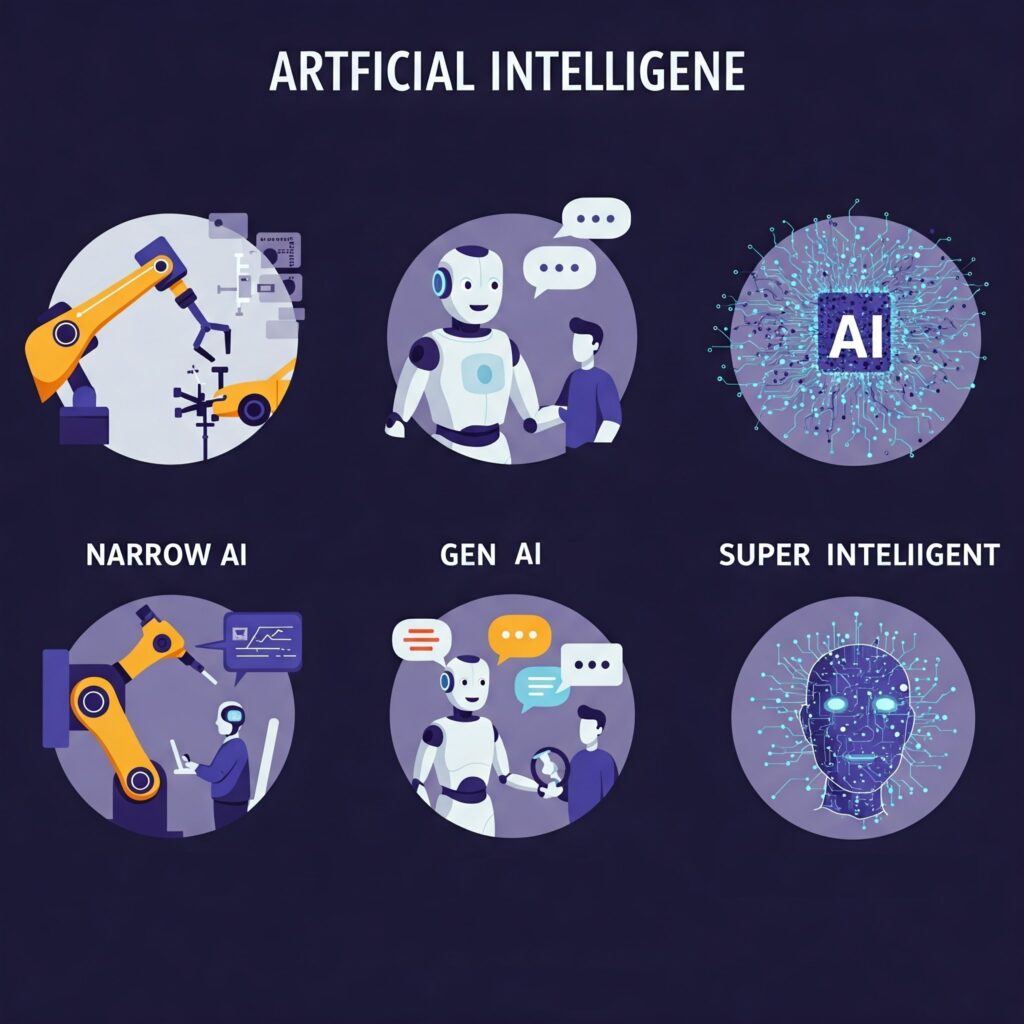
- Narrow AI (or Weak AI): This is the type of AI we see and use most often today. Narrow AI is designed and trained for a specific task. Examples include Netflix’s recommendation system suggesting movies you might like, voice assistants like Siri answering your questions, and spam filters identifying unwanted emails. These systems excel at their specific functions but cannot perform tasks outside their defined scope.
- General AI (or Strong AI): This is a hypothetical type of AI with human-level cognitive abilities. A General AI would be able to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, just like a human. Currently, General AI does not exist.
- Superintelligent AI: This is also a hypothetical future form of AI that would surpass human intelligence in all aspects, from creativity to problem-solving. The possibility and implications of superintelligent AI are subjects of much debate and research.
Bonus (Alternative Classification):
- Reactive Machines: These are the most basic types of AI. They react to the present situation based on pre-programmed rules and do not have memory of the past. A classic example is Deep Blue, the IBM computer that defeated a world chess champion.
- Limited Memory: These AI systems can store some information about the past to make better decisions in the future. Self-driving cars, which need to remember the speed and location of other vehicles, fall into this category.
- Theory of Mind: This is a future stage of AI that would understand that other entities (humans, other AIs) have beliefs, desires, and intentions that can affect their behavior. This level of understanding is crucial for complex social interactions.
- Self-aware AI: This is a hypothetical future form of AI that would have consciousness, self-awareness, and understand its own existence. This is a highly debated and currently theoretical concept.
Subfields of AI (With Simple Definitions)
The field of Artificial Intelligence is vast and encompasses several specialized subfields:
- Machine Learning (ML): A core part of AI that focuses on enabling computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subfield of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to analyze complex data like images, text, and audio.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It powers chatbots, translation services, and sentiment analysis.
- Computer Vision: Allows computers to “see” and interpret visual information from images and videos, used in facial recognition and object detection.
- Robotics: Combines AI with engineering to create intelligent robots that can perform tasks autonomously.
- Expert Systems: AI systems designed to mimic the decision-making ability of a human expert in a specific domain.
Where Do We Use AI Today?
AI is no longer confined to research labs; it’s integrated into numerous aspects of our lives:
- Healthcare: Assisting in diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
- Education: Providing personalized learning experiences and automated grading.
- Banking & Finance: Detecting fraud, assessing credit risk, and offering personalized financial advice.
- Transportation: Powering self-driving vehicles, optimizing traffic flow, and improving logistics.
- Customer Service: Handling inquiries through chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Social Media: Filtering content, personalizing feeds, and detecting harmful content.
- Everyday Life: From voice assistants and spam filters to smart home devices and personalized recommendations, AI is constantly working behind the scenes.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
The increasing adoption of Artificial Intelligence brings numerous benefits:
- Saves Time and Effort: Automating repetitive tasks frees up human potential for more creative and strategic work.
- Reduces Human Error: AI systems can perform tasks with greater accuracy and consistency than humans.
- Can Handle Large Data Sets: AI excels at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data to extract valuable insights.
- Helps in Innovation: AI can accelerate scientific discoveries, like identifying potential drug candidates in medical research.
Risks and Ethical Concerns
Despite its benefits, Artificial Intelligence also raises important risks and ethical concerns that need careful consideration:
- Job Displacement: Automation driven by AI could lead to job losses in certain sectors.
- Bias and Discrimination in AI Models: If AI systems are trained on biased data, they can perpetuate and even amplify societal inequalities.
- Lack of Transparency: The decision-making processes of complex AI models can be difficult to understand, raising concerns about accountability.
- Safety and Control: As AI systems become more autonomous, ensuring their safety and maintaining human control is crucial.
The Future of AI
The field of Artificial Intelligence is constantly evolving, and its future holds immense potential. We can expect to see even more sophisticated AI applications across various industries. The impact on humanity could be transformative, influencing everything from how we work and live to how we interact with technology.
The importance of human-AI collaboration will likely grow, with humans and AI working together to achieve outcomes greater than either could achieve alone. The role of global regulation will also be critical in ensuring the responsible and ethical development and deployment of Artificial Intelligence.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a powerful and rapidly advancing technology that is already reshaping our world. Understanding its fundamental concepts, from its definition and how it works to its various types and ethical implications, is essential for everyone. While AI offers tremendous potential for progress and innovation, it’s crucial to address the associated risks and ethical concerns proactively. By continuing to learn about Artificial Intelligence and engaging in thoughtful discussions about its future, we can help ensure that this transformative technology benefits all of humanity.
People Also Ask:
What is the main purpose of AI? The main purpose of AI is to create computer systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making, ultimately aiming to automate processes, enhance human capabilities, and drive innovation.
Can a beginner learn AI? Yes, a beginner can definitely learn the fundamentals of AI. There are numerous online courses, tutorials, and resources available that cater to individuals with no prior experience. Starting with the basic concepts and gradually exploring specific subfields like Machine Learning is a good approach.
Will AI replace humans? While AI will undoubtedly automate many tasks, the idea of it completely replacing humans is a complex and ongoing debate. It’s more likely that AI will augment human capabilities, creating new job roles and transforming existing ones rather than causing mass unemployment across all sectors.
How is AI used in daily life? AI is integrated into many aspects of daily life, including voice assistants (like Siri and Alexa), recommendation systems (on Netflix and Amazon), navigation apps (like Google Maps), spam filters in email, facial recognition on smartphones, and personalized news feeds on social media.